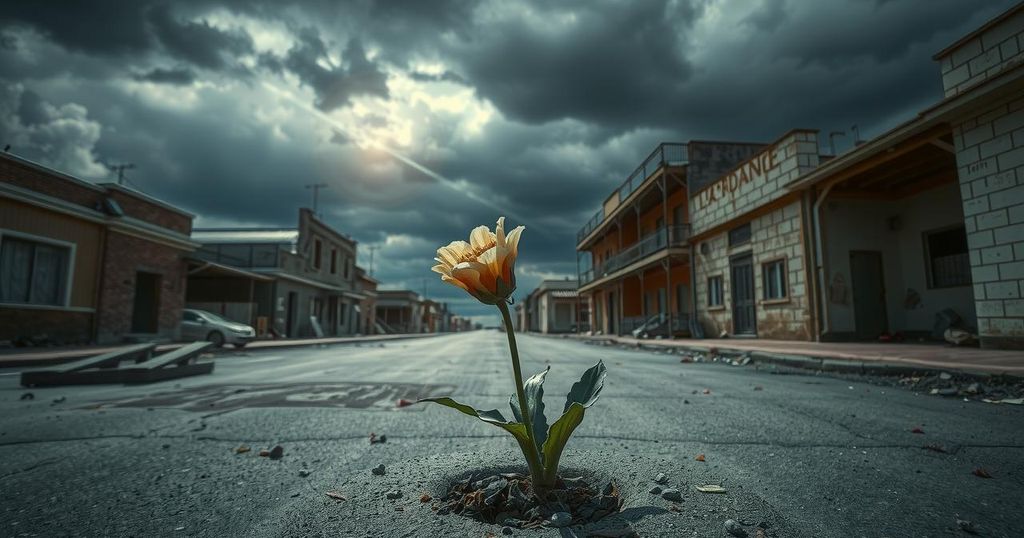
The Democratic Republic of Congo is experiencing a deadly insurgency as the M23 rebel group intensifies its campaign for control, particularly around Goma. The conflict has caused crises including mass displacements and severe humanitarian conditions. International reactions are mixed, with concerns over Rwanda’s involvement and China’s significant economic interests in the region.
A severe insurgency is currently engulfing the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), a nation abundant in minerals essential for modern technology. The rebel faction M23 is intensifying its campaign, advancing southward from Goma, marking a significant escalation in a conflict that has persisted for over a decade. The United Nations has cautioned that the conflict may destabilize the region even further, despite prior attempts at peace.
Following M23’s recent seizure of Goma, the group’s leader, Corneille Nangaa, has expressed intentions to extend the conflict towards the capital, Kinshasa. In response, the Congolese government has mobilized its forces, with President Félix Tshisekedi pledging to restore control across all territories. The DRC has faced continuous warfare for decades, with the latest unrest escalating since early January 2023, displacing more than 400,000 individuals last month.
The ongoing violence has seen numerous casualties, including several United Nations peacekeepers in Goma. The Congolese administration has characterized the M23’s actions as a declaration of war from Rwanda. In Goma, dire conditions have emerged, with bodies in the streets, alongside prolonged outages of water and electricity affecting residents’ access to food.
International reactions to this humanitarian crisis have been mixed. Reports indicate that Romanian mercenaries deployed to assist the Congolese forces had to seek shelter with the United Nations following an intense retreat. French Foreign Minister Jean-Noël Barrot’s recent visit underscores the global concern, which has heightened amidst local protests demanding stronger action from the international community.
M23, founded in 2012, primarily comprises ethnic Tutsi rebels, with roots in historic tensions between Tutsi and Hutu groups. While Rwanda has faced allegations of providing military support to M23, the rebel group asserts that the Congolese government is failing to protect ethnic Tutsis. Previous peace agreements have yielded little stability, leading to an environment necessitating clarity in both domestic and international policy regarding the DRC.
China plays a critical role in the DRC, especially concerning its mineral wealth, which is increasingly dominated by Chinese enterprises. The country invests heavily in the DRC’s cobalt production, essential for global electronics. While the conflict affects local mining operations, experts suggest that immediate threats to global mineral supply remain minimal despite the chaos.
Rwanda’s involvement in the conflict has generated significant international scrutiny, particularly after the M23’s rapid advance in Goma. The DRC government and international observers have pondered the ongoing support Rwanda receives despite its controversial actions. Some Western nations are reassessing ties with Rwanda, highlighting ongoing diplomatic tensions amidst this crisis.
Overall, the DRC faces a complex interplay of local conflicts, international interests, and humanitarian crises, with implications that extend well beyond its borders. The international community’s response will be crucial in shaping the future stability of the region, as well as in determining the fate of its vast mineral resources.
The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) has been embroiled in conflict since its independence from Belgium in 1960, with various factions vying for control amid rich mineral resources. The M23 rebel group has gained significant attention due to accusations of backing from Rwanda, contributing to a longstanding ethnic conflict primarily between the Tutsi and Hutu populations. The region has faced immense humanitarian issues, with millions displaced and thousands affected by violence, impacting not only local stability but also global mineral supply chains.
The ongoing conflict in the DRC, marked by M23’s aggressive expansions, poses serious humanitarian and geopolitical challenges. With territories under siege and significant displacement of populations, the international community’s response remains essential for future stability. The DRC’s mineral wealth complicates the situation, attracting global interests while necessitating careful diplomatic engagements to mitigate regional tensions and humanitarian crises.
Original Source: www.nbcnews.com