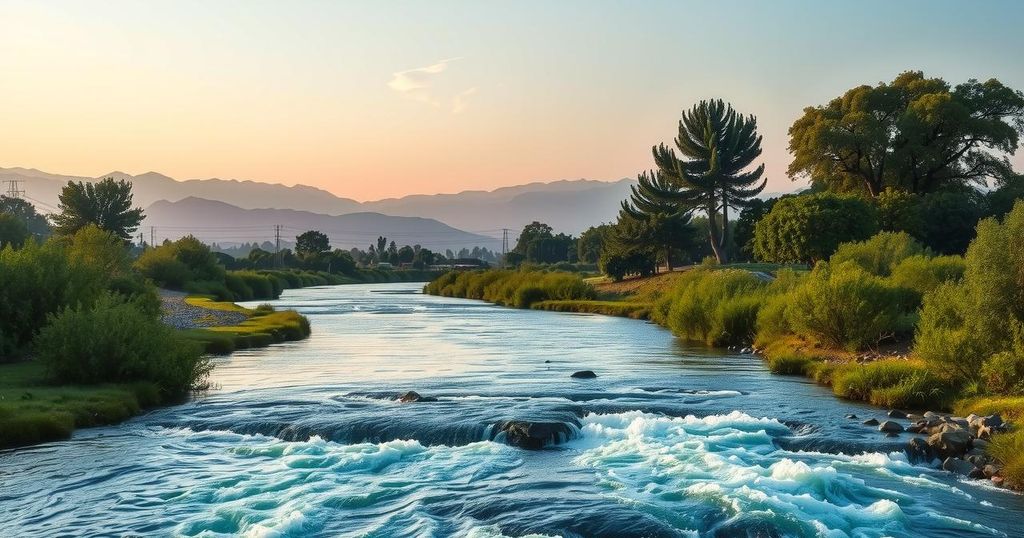
Egypt is expressing alarm over a recent agreement between Ethiopia and Israel to enhance cooperation in water and energy sectors. This deal comes amidst ongoing tensions regarding the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam, which threatens Egypt’s water security. Experts warn that this cooperation may exacerbate Egypt’s challenges with water access, indicating a need for strategic countermeasures to ensure sustainability in the face of potential adversities stemming from the dam’s impact.
Alarm is rising in Egypt following a recent agreement signed on February 4 between Ethiopia and Israel that enhances cooperation primarily in water management and energy development. This pact deepens existing ties while relations between Egypt, Ethiopia, and Israel continue to deteriorate. Egyptian observers worry that these moves could have negative implications for their country, especially amid ongoing tensions regarding Ethiopia’s Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD) on the Nile, Egypt’s main freshwater source.
The construction of the GERD, which Ethiopian President Abdel Fattah al-Sisi has labeled an “existential threat” to Egypt, raises significant concerns for the country regarding its water supply. The Grand Dam has created a reservoir larger than London and threatens to drastically reduce the annual water share that Egypt relies on from the Nile. Following a decade of fruitless negotiations involving Sudan, Egypt fears that the dam will cause severe economic damage as it limits the flow of water from the Nile.
Experts indicate that the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam significantly obstructs Nile water flow, particularly during its reservoir filling phase. Professor Abbas Sharaqi highlighted that Egypt invests substantial resources annually to mitigate adverse effects stemming from the dam’s construction, crucial as the nation already faces a deficit of around 7 billion cubic meters in its water supply.
To address these challenges, Egypt is initiating multiple strategies, such as investing in seawater desalination plants and enhancing its irrigation systems to conserve water. These initiatives aim to counterbalance the negative impact of the GERD while also facilitating agricultural transformation in the country. Sharaqi noted these measures, albeit costly, contribute to alleviating the water deficit exacerbated by Ethiopian actions.
The historical context between Egypt and Israel has evolved from hostility to a tenuous peace characterized by strategic cooperation. However, recent tensions linked to Israeli actions in Gaza and U.S. policies regarding Palestinian refugees have strained this relationship. Amidst these challenges, Egypt grows increasingly concerned about the deepening collaboration between Ethiopia and Israel in water management and agriculture, particularly as Egypt’s security and water supply heavily depend on the Nile.
Officials in Egypt have stated that they view Ethiopia’s growing connection with Israel as a potential strategy to undermine Egypt’s stability by limiting its access to vital Nile waters. Reports have emerged suggesting that the U.S. administration might leverage the GERD for political gains, further compounding Egypt’s apprehensions. While there has been no official response from Egypt regarding the Ethiopia-Israel cooperation deal, internal observers express concern about its possible implications for Egyptian sovereignty and water security.
Concerns are especially heightened by the perception that the size of the GERD does not align with Ethiopia’s stated intentions of generating electricity. Critics argue that the dam’s dimensions suggest a potential political agenda rather than solely a developmental one, leading to speculation about Ethiopia’s long-term intentions. Sharaqi highlighted that the excessive scale of the dam implies an ambition beyond purely energy generation, warranting further scrutiny of Ethiopia’s plans and their ramifications for Egyptian water security.
Egypt is increasingly alarmed by the growing cooperation between Ethiopia and Israel, particularly in water and energy sectors, amid the ongoing crisis surrounding the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam. The implications of this development could severely impact Egypt’s already strained access to Nile waters. Experts stress the existential threat posed by the dam, highlighting the urgent need for effective strategies to mitigate its adverse effects on Egypt’s water supply. Amid deteriorating regional relations, the prospect of further Israeli-Ethiopian cooperation raises significant concerns for Cairo’s national security.
Original Source: www.newarab.com