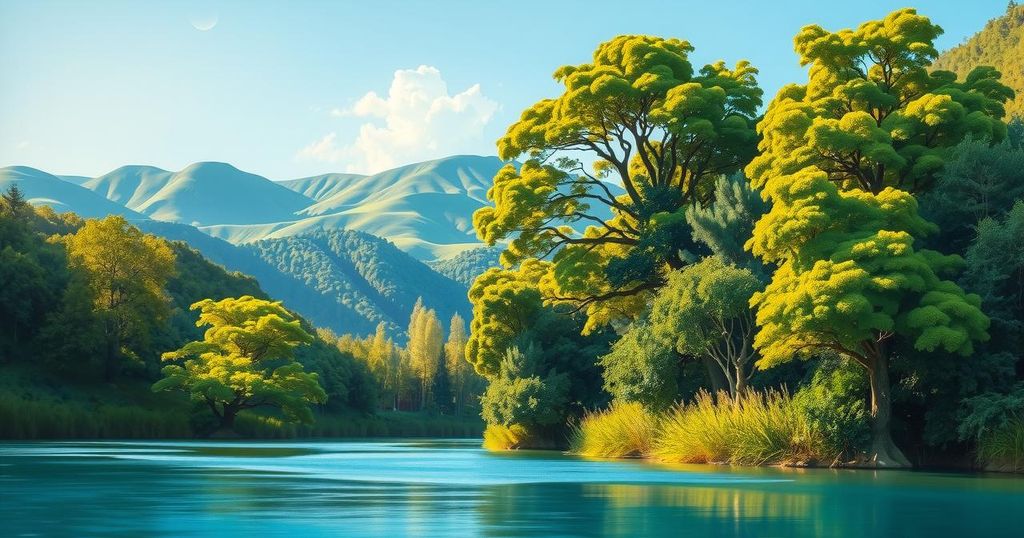
Guyana’s Interior Minister warned that support for Venezuela’s planned elections in the disputed Essequibo region could lead to treason charges. The tensions have escalated due to recent border incidents and an appeal to the International Court of Justice by Guyana to prevent the elections. Venezuela’s actions are seen as a violation of past agreements, with both nations having a long history of conflict over the territory.
Guyana’s Interior Minister, Robeson Benn, has issued a stern warning that any individual, either a citizen or resident, who supports Venezuela’s upcoming elections in the contested Essequibo region will face treason charges. Benn highlighted the intentions of Venezuelan President Maduro to appoint local officials and warned of consequences for those collaborating with such plans.
Furthermore, Minister Benn noted that although there is a lenient policy towards individuals with familial connections to Venezuela, endorsement of the electoral process by Venezuela will not go unpunished. He cited recent actions, including denying entry to 75 Venezuelan migrants, as evidence of increased scrutiny.
The tensions between Guyana and Venezuela have escalated due to recent incidents, such as a Venezuelan naval vessel’s incursion into Guyanese waters and the shooting of six Guyanese soldiers. Last week, Guyana sought intervention from the International Court of Justice to halt Venezuela’s electoral plans in Essequibo.
In a recent announcement, Venezuela’s Interior and Justice Minister, Diosdado Cabello, indicated that Venezuela will not only appoint a governor but also elect eight legislators from Essequibo. This announcement follows a unilateral referendum from Venezuela to annex the region, exacerbating an already strained relationship, as Guyana has governed Essequibo since 1966.
Guyana asserts that these elections infringe upon the Argyle Agreement signed in December 2023, which calls for both countries to avoid escalating tensions over territorial disputes. The origins of the conflict trace back to the 1899 Paris Arbitration Award, which recognized British Guiana’s sovereignty over the area.
In summary, Guyana firmly opposes Venezuela’s planned elections in the Essequibo region, deeming any support for such actions as treasonous. This dispute is deeply rooted in historical claims and legal agreements, and ongoing tensions highlight the complexity of the relationship between the two nations. Guyana’s appeal to the International Court of Justice further underscores its commitment to resolving the territorial issue through legal channels, despite Venezuela’s rejection of the court’s authority.
Original Source: efe.com